NAT Firewall: What Is it and What Are its Benefits?

Arsalan Rathore

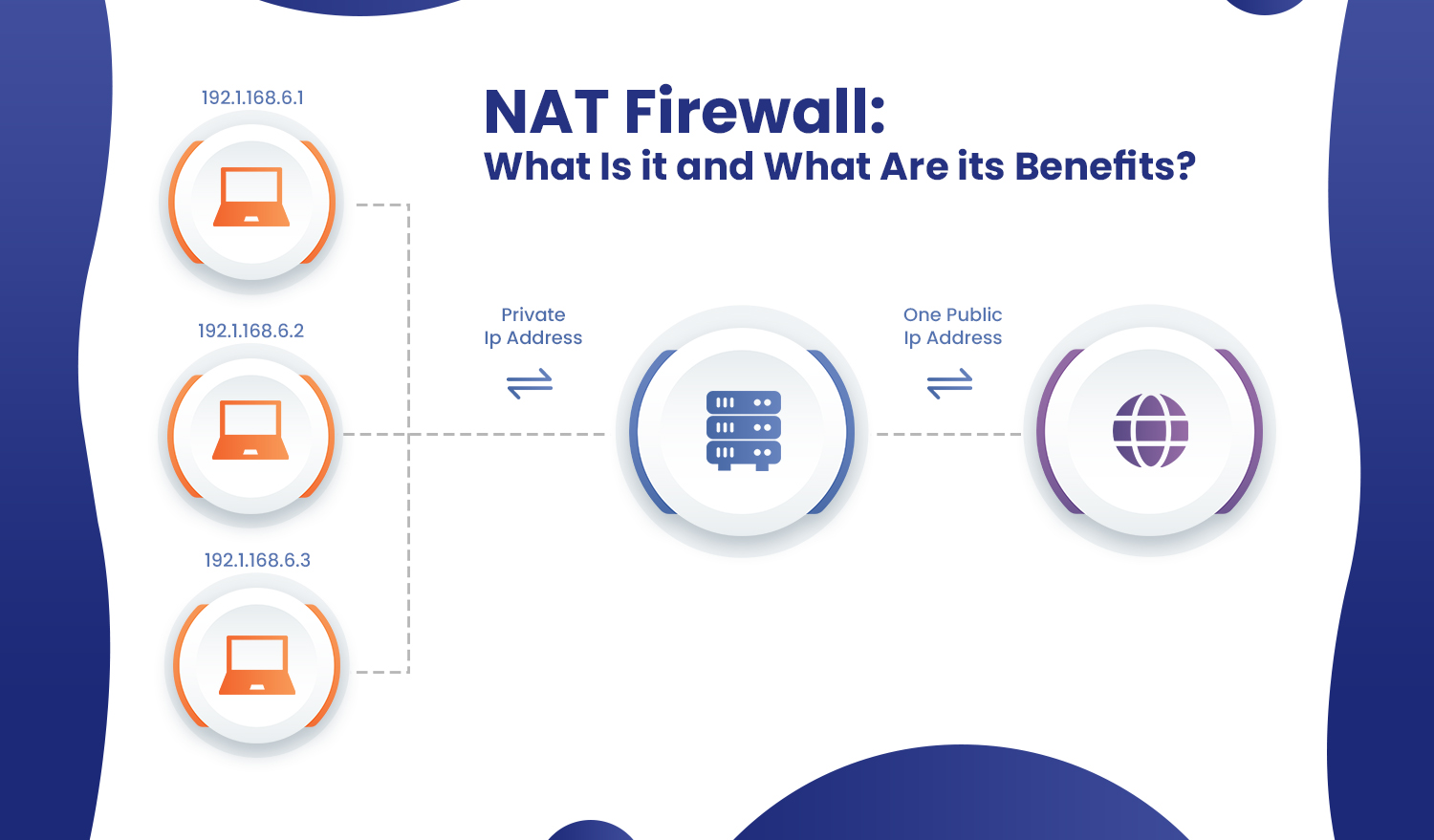
Changing a private IP address into a public IP address is called Network Address Translation (NAT). This can be done to either one or multiple local IP addresses, and the conversion can be made directly into a global IP address.
Through these IP addresses, local devices, hosts, and other such servers, can be made to access the internet at large. All NATs work on firewalls or router-based systems to protect the private connection, and all the devices that connect to this network will have different private IP addresses with the same public IP address.
These measures add to personal security and connectivity to ensure the user remains safe and secure at the best internet speeds. Read on to learn more about how NAT firewalls work and their benefits!
Table of Contents
Types of NAT (network address translation)
Static NAT
This is the simplest form of NAT, which merely translates IP addresses one by one. For example, a private IP address used internally (192.162.20.1) is translated to a public IP address (12.15.65.05). This configuration is often used in web hosting.
Dynamic NAT
In this NAT configuration, a number of private IP addresses are mapped to a set of shared public IPs. It’s used when we know how many people at a specific location simultaneously intend to access the Internet.
The router shares a group of public IP addresses between its connected devices with dynamic NAT. It also includes directly mapping private IP addresses to public IP addresses. Here, the IP address is assigned to the device making the internet connection request. So, the connection is first-come, first-served.
Port Address Translation (PAT)
NAT overload is another name for this configuration. A single external IP address can replace many private (local) IP addresses. The port number is utilized for each IP address to identify the corresponding communication. One real global (public) IP address can be shared among thousands of users, making this method the most popular.
What is NAT Firewall?
In the most basic terms, A NAT firewall works by permitting traffic to pass over a network and to the device only if requested. It operates on a router to offer network-wide protection to all connected devices. Doing this anonymizes the network since the IP addresses aren’t shared with the internet.
Since the IP address can reveal personal information about the user, such as their general physical location or online activities, anonymization doubles as a privacy feature. This basis of privacy is maintained whenever the firewall is protected.
How Does A NAT Firewall Work?
A NAT firewall converts private IP addresses into public IP addresses. Whenever data packets are sent across servers due to user requests, the firewall ensures the user’s privacy and security by protecting this data on their devices and networks.
Anytime data packets from the outside network make their way to the internal network, the NAT firewall will prohibit any unwanted or malicious add-ons. If inbound internet traffic doesn’t have a private IP address beyond the gateway, the NAT firewall discards it as unsolicited.
By doing this, the firewall minimizes attacks by hackers and cybercriminals that could have come through unauthorized and insecure connections.
Also Read: VPN Vs. Firewall – Main Differences and Uses
What Are the Benefits of NAT Firewalls?
1. Enhanced Security
With NAT, the IP addresses of both the sender and the receiver are concealed. The NAT prevents hosts on other networks from communicating with hosts inside the NAT unless the user explicitly permits it. Therefore, NAT adds a new safeguard to a network’s security.
2. Cost Control
By combining NAT with a private IP address, businesses save money by not having to obtain additional private IP addresses for their internal computers. Multiple computers can share the same IP address. As a result, companies can save money.
3. Ensures Private IP Consistency
They have their own internal IPv4 address scheme. Because of this, they will continue using their current addressing system even if you switch to a different one. The user’s internal address modifications will be disabled if they switch ISPs.
4. Flexibility and Tools
The Network Address Translation (NAT) system includes a plethora of backup and load-balancing features. The overall network stability and adaptability will be improved with the aid of these tools.
NAT Firewalls and Torrenting
When torrenting, NAT firewalls can cause issues by preventing unwanted traffic from reaching the user’s end device. As a result, sharing files with other torrent users by uploading (seeding) them can be difficult.
Downloading (leeching) from a large number of peers on the network might also be problematic. So, much as a NAT firewall prevents you from communicating with a large number of people in a torrent swarm, a PAT firewall accomplishes the same.
This doesn’t, however, rule out the possibility of torrenting even behind a NAT firewall. Modern NAT firewalls are typically quite lenient so that they won’t slow down your download or upload speeds. Public facilities like schools and hotels usually have stricter firewalls, although torrenting is unaffected by using a virtual private network (VPN) or a router.
Drawbacks of NAT Firewall
Though using NAT Firewall has some great benefits, at the same time, there are some drawbacks as well that you will have to keep in mind, like:
No Safety from Phishing and MITM
A NAT firewall will not protect you from phishing fraud, which is a significant drawback. When a service requires you to join via a link provided in an email, and it’s not actually by the service provider but rather the hacker, the NAT Firewall cannot block it. That’s because it’s just an email, and the NAT Firewall does not have the capability of blocking it in any way.
Furthermore, you will not be protected from a man-in-the-middle attack by using a NAT firewall. A hacker sets up a phony WiFi hotspot and attempts to lure you into connecting to it so they may collect your personal information. There’s no way a NAT Firewall can raise a flag in this instance either.
Performance Issues
When a visitor makes a request to a remote server, the NAT router verifies that the request is coming from within the router’s network. However, some hosts restrict the number of simultaneous connections they will allow. Any subsequent requests will be denied if the total number is exceeded. A decrease in performance in real-time protocols is likely to occur.
Memory Consumption
When the service comes in or goes out, the data packets are checked by NAT. The information packets will be translated into local and global IP addresses. The memory will be used to hold the translated data. As a result, this will use up a lot of your computer’s memory.
Issues with Troubleshooting
Using NAT will lessen the ability to track data from beginning to end. Additionally, the IP address will be changed frequently. In turn, this will make troubleshooting more challenging. This will become even more difficult in extreme instances, such as when you are in a really remote place.
Conclusion
The NAT firewall is not as complicated as it may seem. In order to load a website, your device will use its private IP address to contact the router. When the request reaches the router, it is converted before being sent to the server of the site through the latter’s public IP address. The router then forwards the response from the server to your private IP address.
On the other hand, a firewall acts as a barrier to prevent unwanted data exchanges between computers. Therefore, a NAT firewall only lets through the traffic that an endpoint has explicitly requested on the network.
NAT firewalls are excellent for online security because they prevent hackers from accessing your private IP address. The benefits and drawbacks of using a NAT Firewall have been discussed thoroughly in this guide, and it’s evident that the benefits cancel out the drawbacks.

No comments were posted yet