IPv4 vs IPv6: What’s the Difference and Which One is Better

Arsalan Rathore

Internet Protocol addresses (IP Addresses) are like codes that our devices use to connect to one another on the internet. This address is unique to each device that is connected to a computer network, on the condition that the network uses IP protocol for communication. The address looks like a numerical label with either dots or colons which can be used to differentiate the protocol version.
Technically, every location on any network has a unique numerical label attached to it. “Astrill.com” is translated back to a number through DNS, such as 104.103.88.45. This number makes no sense to us, numbers like these are what the internet runs upon! These specific addresses specify the technical formatting of the addressing and packet route.
This means that we can use IP addresses to see the level of security our network can offer us. Sometimes, IP addresses can be combined with a Transmission Control Protocol. TCPs can allow for the creation of a virtual connection between any two points, allowing users to have more control over the exchange of data.
IPv4 and IPv6 are the two most popular generations of Internet Protocol. The ‘v’ stands for version and the following number is to denote their editions- so we can tell that IPv4 came before IPv6.
Table of Contents
What is IPv4?
IPv4 is one of the first protocols used on packet-switched Link Layer networks, such as Ethernet. This is crucial for standards-based interworking methods on the internet, and its first version was integrated in 1983, for the production of ARPANET.
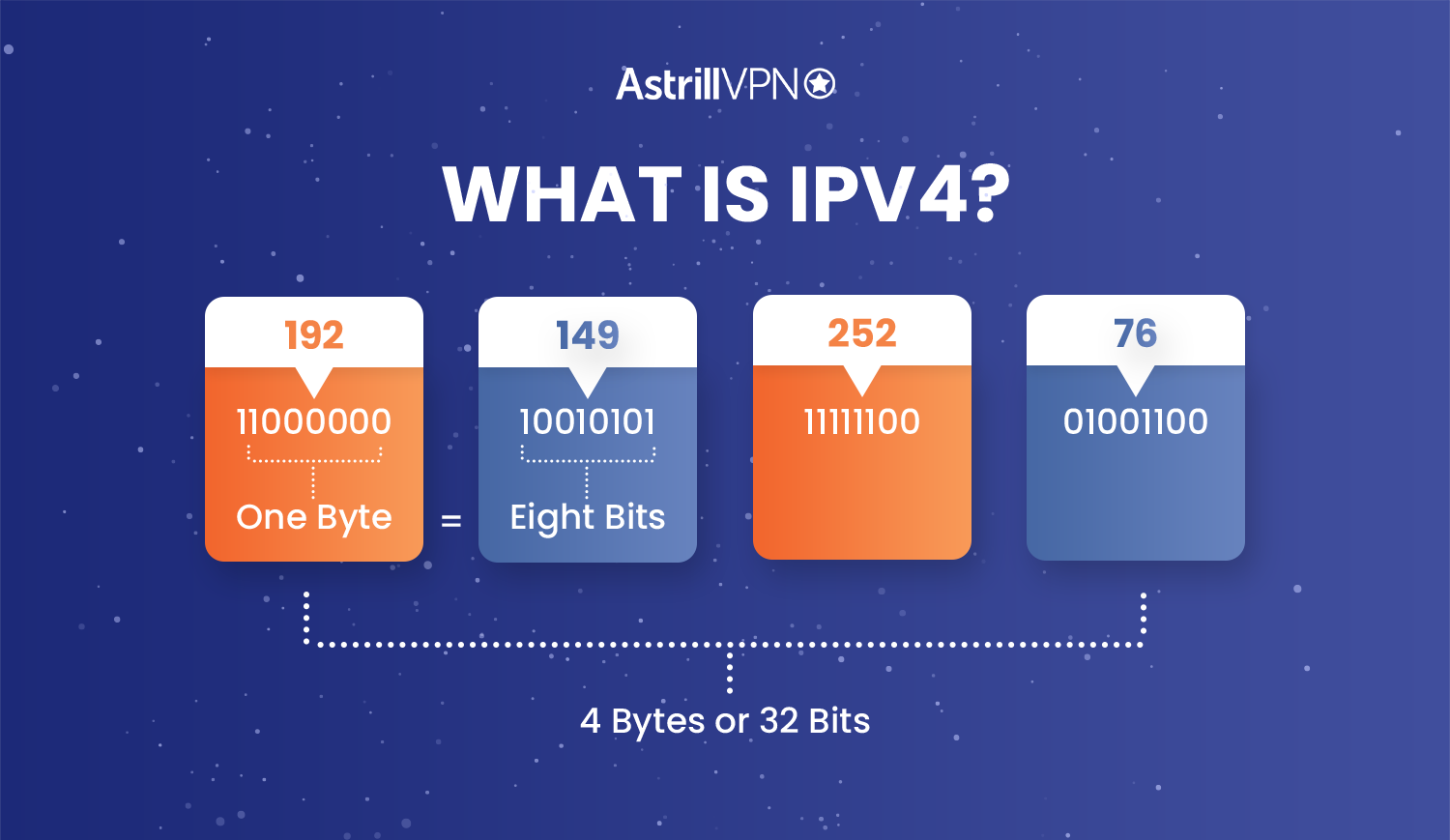
IPv4 users get to utilize the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server to create a connection every time they log into any network. This is called stateful auto-configuration and is a type of address assignment process.
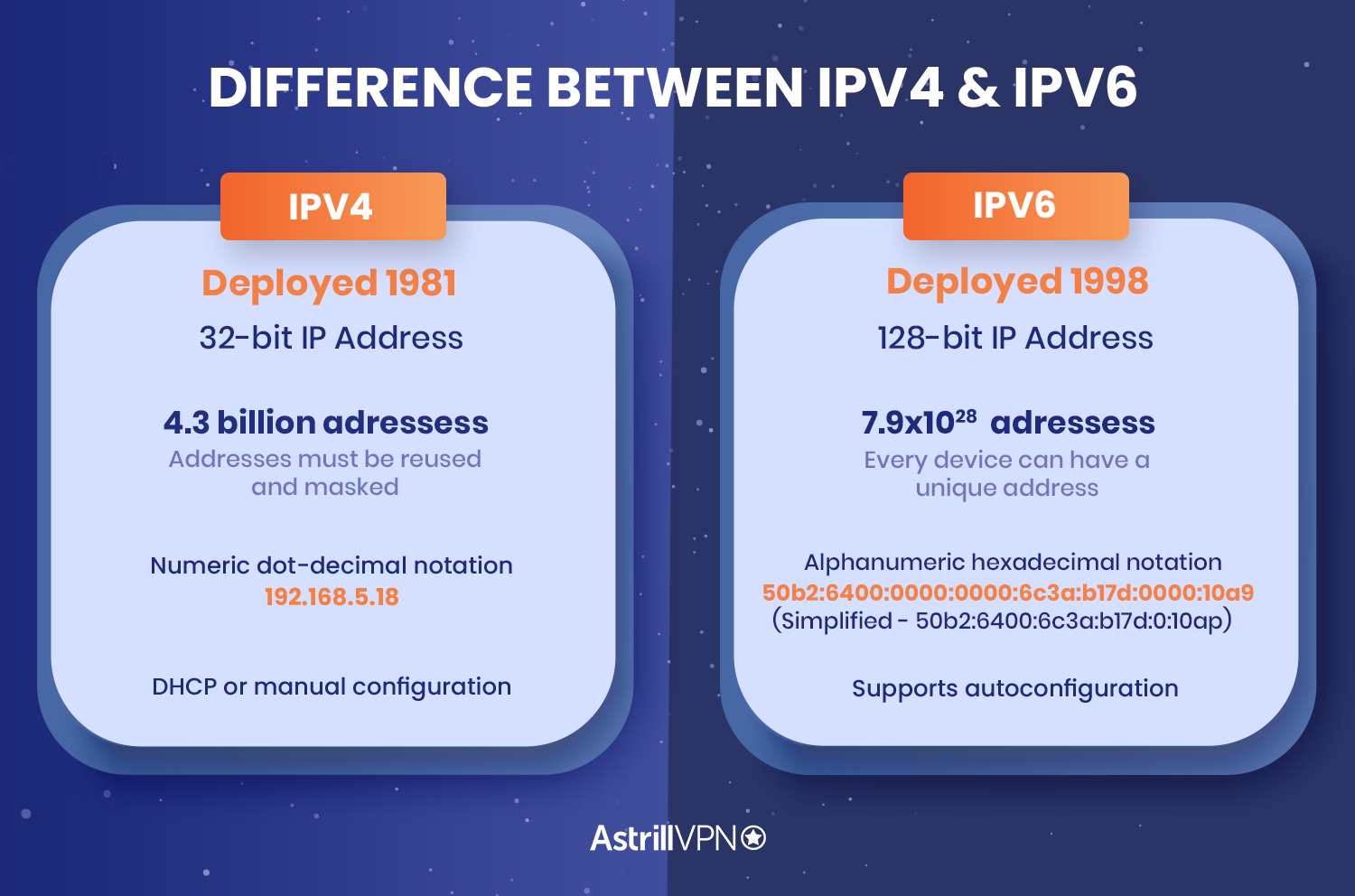
This protocol uses a 32-bit source with a destination address field that can go up to 4.3 billion addresses. As each address is unique to a single destination, you could imagine that the growth of the internet meant that addresses were quickly running out. This issue was only made more prominent with the widespread use of smartphones and gaming devices that could connect to the internet.
Truth is, no amount of clever solutions from engineers could actually solve the inherent problem of IPv4’s destination address limitation. Hence, the creation of IPv6 was established mainly due to the fact that IPv4 addresses were simply running out.
Features of IPv4
- In IPv4, IP addresses look like four one-byte decimal numbers, separated by a dot. Such as 182.178.1.1.
- IPv4 allows connectionless protocol by creating a layer of simple virtual communication over a variety of devices
- IPv4 uses less memory which allows for ease of access in remembering different addresses
- Because it’s been in use for so long, it’s already supported by a greater number of devices
What is IPv6?
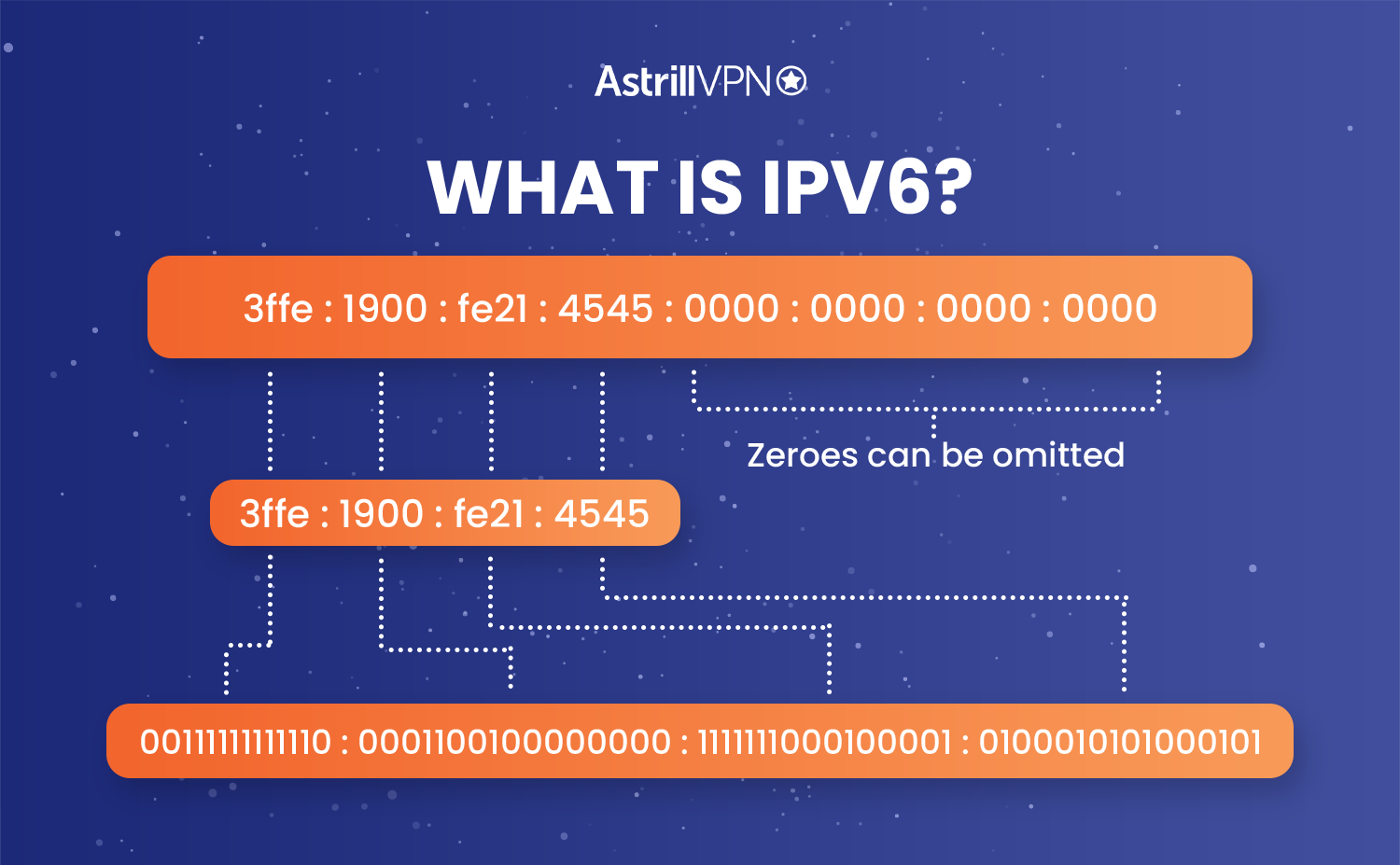
IPv6 was initially created to tackle the issue of limited addresses in IPv4. It was developed by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to solve not only the capacity issues but also to introduce better, refined features. One of the main differences between IPv4 and IPv6 is that the successor offers unlimited addresses. IPv6 also uses 128-bit IP addresses.
As it is the successor for IPv4, IPv6 utilizes the new and improved DHCPv6 protocol that supports stateful auto-configuration and also stateless auto-configuration of nodes. Stateless auto-configuration uses router advertisements to create individualized addresses and it doesn’t need access to a DHCP server to obtain these addresses.
Because of how snappy and quick DHCPv6 is, it has created a great amount of convenience in its use. It allows users to simply log in and get to their work immediately by simplifying address management and administration.
Learn more: Find out if your computer leaks IPv6 address
This means that, by extension, IPv6 allows for automatic address configuration, as well as reconfiguration, allowing administrators to renumber the network addresses of clients without needing to access them.
Features of IPv6
- IP addresses belonging to IPv6 IP look like hexadecimal numbers which are separated by colons (eg: fe80::d4a8:6435:d2d8:d9f3b11)
- IPv6 has hierarchical addressing and routing infrastructure which allows for convenient organization of data
- IPv6 can take advantage of both, stateful and stateless configuration, which can allow users to enjoy a seamless browsing experience
- Since it is newer, there is the greater customer support which enhances its quality of service
In addition to this, IPv6 was designed keeping end-to-end encryption in mind. As it grows in popularity, the difficulty of hijacking cybercrimes such as man-in-the-middle attacks will increase. Moreover, it also supports more-secure name resolution as the Secure Neighbour Discovery (SEND) protocol adds a layer of protection to Neighbour Discovery Protocol (NDP). Together, it works with cryptographic methods that are independent of IPsec, offering the user more security than ever before.
Should I use IPv4 or IPv6?
Now that we’ve dived well into the comparison, the question is should you use IPv4 or IPv6?
IPv4 is the fourth version of IP, whereas IPv6 is the most recent version. As it follows, IPv6 is more advanced, more secure, and much faster in comparison to IPv4. Take a quick look on the sidebyside comparison:
| Features | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|
| Address format | 32-bit decimal format (e.g., 192.0.2.1) | 128-bit hexadecimal format (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334) |
| Address space | Limited to about 4.3 billion unique addresses | Enormous, with approximately 3.4 × 10^38 unique addresses |
| Header length | Fixed length (20 bytes) | Variable length (40 bytes minimum) |
| Fragmentation | Hosts and routers can fragment packets | Fragmentation is done by the source host |
| Quality of Service (QoS) | Support for QoS is optional and not commonly used | Support for QoS is mandatory and includes traffic class and flow label fields |
| Address autoconfiguration | Uses DHCP or static addressing | Uses Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) or DHCPv6 |
| Security | No built-in security features | Built-in support for IPsec and mandatory implementation of extension headers for secure routing |
| DNS support | Requires DNS for name resolution | Includes support for name resolution through DNS and multicast DNS |
| Deployment | Widely deployed and supported | Slow adoption due to compatibility issues and lack of immediate need for more addresses |
| Compatibility | Can’t interoperate with IPv6-only devices | Can interoperate with both IPv4 and IPv6 devices using translation mechanisms such as dual-stack and NAT64 |
| Packet flow identification | Identification field only | Flow Label field in addition to Identification field |
| Checksum field | Optional | No checksum at the IP layer (checksum handled at higher layers) |
| Transmission scheme | Best-effort delivery | Supports both best-effort and Quality of Service (QoS) delivery |
| Encryption, and Authentication | Optional (IPSec) | Required (IPSec) |
| Number of octets | 32 bits | 128 bits |
| End-to-end connection integrity | Not guaranteed | Guaranteed with IPSec |
| Number of IP addresses | Approximately 4.3 billion | Approximately 3.4×10^38 |
If seamless connectivity amongst multiple devices is a priority for you, IPv6 seems like a better option. This is because of interoperability and configuration capabilities that allow the hardware to assign multiple IP addresses to the same device by itself. However, if you enjoy browsing older archives and require access to such content, IPv4 may be more useful simply because of its age.
IPv6 was primarily built with security in mind, and it is integrated with IPSec protocols for security, authentication and verification, and data integrity. IPSec can also be integrated into IPv4, but that is up to the network service provider or the users themselves.
Is IPv6 faster than IPv4?
Due to the technological advancements of IPv6, in theory, it is much faster. This is because it doesn’t waste any time on Network Address Translation and focuses more on autoconfiguration.

However, since IPv4 has been around for so long, its networks are mature and highly optimized. IPv6 also uses larger packets which can slow down connection speeds, especially on unoptimized platforms. But this is something that can only be solved with time, increased accessibility, and technical fine-tuning.
How to Protect your IP address
The most secure way to protect your IP address and any online activity is to use AstrillVPN. It is an application that masks your IP address and encrypts all of your traffic to hide you from hackers and organizations looking to collect, store, or sell your data.
After this, it is advised to monitor all network activities with a firewall that can make use of a packet filter. This is to inspect IP packet headers to make sure that there is no malicious activity going on. It is also a good idea to only visit secure websites that make use of HTTPS protocols, and to never share passwords or sensitive information with anyone.
When looking at IPv6 vs IPv4, we can notice that both offers varied security protections. IPv6 was created with end-to-end encryption in mind, so the use of this protocol will prevent and minimize attacks coming from any direction. This makes IPv6 as a no-hassle, no-nonsense solution to enhancing security.
Due to the rapidly developing environment of the technology industry, new and more secure configurations are constantly being developed for IPv4 networks. This allows IPv4 networks to be just as secure as IPv6, when configured properly. It is always a good idea to revisit any existing configurations to tie any loose ends when it comes to your online safety.
Other measures include:
- Make use of SSL certificates to help verify the authenticity and safety of websites attempting to connect to your network.
- Use strong and secure passwords to keep all hackers out of your sphere.
- Configuring a firewall to protect your device against unauthorized IP packets, fake IP addresses, suspicious traffic, and any attempts at spying on your activities.
- Making use of a trustworthy antivirus will help you protect your device from any intruders, viruses, or hackers’ attempts at holding your data for ransom.
Which one is better? — IPv4 or IPv6
If you want something that is already configured with the top security protocols, IPv6 is the best option for you. This comes with the temporary drawback of possibly slower speeds but offers total peace of mind for security.
If you do not have access to IPv6, then you can still configure your existing IPv4 network to function just as securely as any IPv6 network. This will take some effort and knowledge, but it can be done for the sake of maintaining your online privacy.

No comments were posted yet