VPN Security: Ultimate Guide to Safe and Private Internet Access

Arsalan Rathore

Internet security is no longer a concern limited to large organizations or tech professionals. Every time you connect to the internet, your data travels through multiple networks, servers, and systems that you do not control. This is where VPN security becomes essential.
A Virtual Private Network, or VPN, is designed to protect your online activity by creating a secure and private connection between your device and the internet. When implemented correctly, VPN security helps safeguard sensitive data, hide your real IP address, and reduce exposure to tracking, surveillance, and cyber threats.
This guide explains what VPN security is, how it works behind the scenes, and why choosing a secure VPN matters more than ever. Whether you are browsing at home, working remotely, or using public WiFi, understanding VPN security allows you to make informed decisions about your online privacy.
Table of Contents
What Is VPN Security?
VPN security refers to the technologies and practices that protect your internet connection and online data when using a VPN. It focuses on keeping your information private, concealing your identity, and protecting your communication from interception or misuse.
At its core, VPN security is not just about hiding your IP address. It is about creating a controlled, encrypted pathway for your data so that only you and the intended destination can access it.
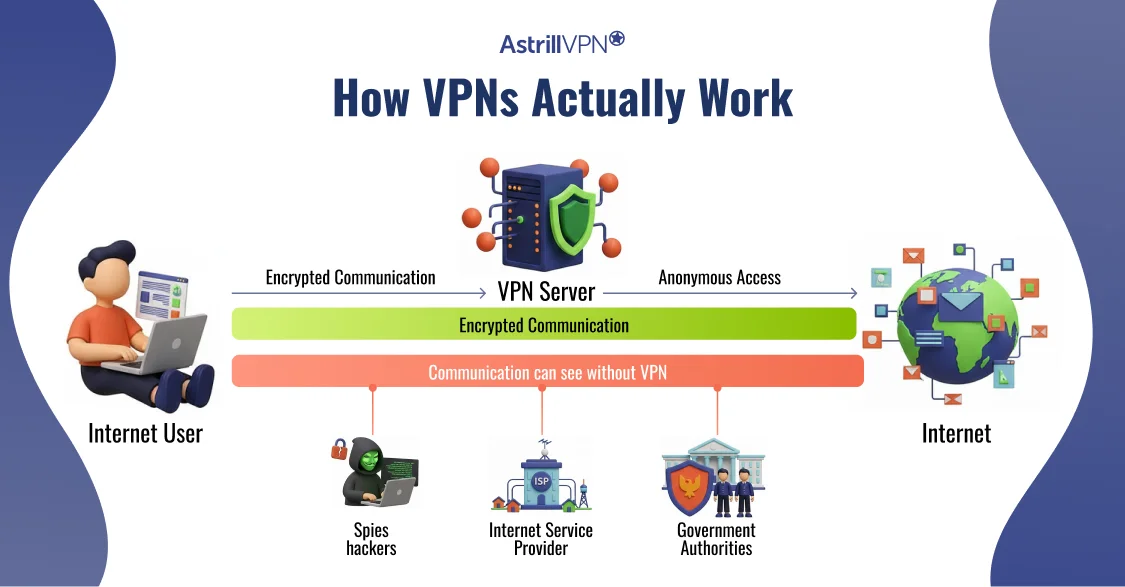
VPN security is the process of securing internet traffic by encrypting data and transmitting it through a protected tunnel between your device and a VPN server. This prevents third parties such as hackers, network administrators, or internet service providers from reading or manipulating your data while it is in transit.
When a VPN is active, your device connects to a VPN server using secure protocols. These protocols establish an encrypted connection that shields your online activity from external visibility. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be understood without the correct decryption keys.
From a security perspective, a VPN also acts as an access control layer. Your real IP address is replaced with the IP address of the VPN server, which helps protect your identity and location. This combination of encryption, tunneling, and authentication is what defines strong virtual private network security.
Why VPN Security Matters in Today’s Online World
Modern internet usage exposes users to risks that were far less common a decade ago. Public WiFi networks in cafes, airports, hotels, and coworking spaces are often unsecured or poorly protected. Anyone on the same network can potentially monitor traffic or launch attacks against connected devices.
Without VPN security, data transmitted over these networks can be intercepted, including login credentials, emails, and personal messages. This makes public WiFi one of the most common entry points for cybercriminals.
Beyond public networks, internet service providers have visibility into user activity by default. They can track browsing behavior, throttle certain types of traffic, and in some regions, retain or share user data. VPN security limits this exposure by encrypting traffic before it reaches the ISP, preventing detailed tracking of online activity.
There is also the growing issue of digital surveillance and data profiling. Websites, advertisers, and third-party trackers collect extensive data about user behavior. While a VPN is not a complete anonymity tool, a secure VPN significantly reduces passive tracking by masking your real IP address and encrypting traffic at the network level.
VPN Security: How VPNs Actually Work?
Virtual private network security is built on three core components: encryption, tunneling protocols, and authentication. Together, they protect internet traffic from interception, tracking, and unauthorized access.
A secure VPN encrypts data before it leaves your device, sends it through a protected tunnel, and verifies the identity of the server you connect to. Each layer plays a critical role in keeping online activity private.
Encryption: How VPNs Protect Your Data
Encryption converts readable data into coded information that cannot be understood without the correct decryption key. When a VPN is active, all traffic between your device and the VPN server is encrypted.
Secure VPNs use modern encryption standards that cybersecurity professionals widely trust.
Common encryption standards used by secure VPNs include:
- AES-256, which provides a high level of protection and is considered industry standard
- ChaCha20, which offers strong security with better performance on mobile and low power devices
VPN Protocols and Security Levels
VPN protocols define how encrypted data is transmitted between your device and the VPN server. The protocol used directly affects security, performance, and reliability.
Widely used secure VPN protocols include:
- OpenVPN: Open source, heavily audited, and known for strong security and flexibility
- WireGuard: Lightweight, modern, and built with a smaller codebase to reduce attack surfaces
- IKEv2 with IPSec: Stable and reliable, especially for mobile connections that frequently change networks.
AstrillVPN Proprietary Protocols
AstrillVPN offers proprietary protocols designed for environments where standard VPN connections may not work reliably.
Masks VPN traffic to appear as regular internet traffic, helping bypass network restrictions while maintaining strong encryption.
Routes traffic through secure web based connections, offering flexibility in restricted or filtered networks.
Choosing the right protocol is critical. Some protocols prioritize speed, others focus on stability, and some are designed to evade detection. A secure VPN gives users control over this choice.
Authentication and Secure Key Exchange
Authentication ensures that your device connects to a legitimate VPN server. This prevents attackers from intercepting traffic through fake or compromised endpoints.
VPNs use digital certificates to verify server identity before a connection is established. During the connection process, a cryptographic handshake securely exchanges encryption keys.
Key security features include:
- Server certificate verification
- Secure handshakes for session setup
- Perfect Forward Secrecy, which ensures each session uses unique encryption keys
What Makes a Secure VPN?
A single technical feature does not define a secure VPN. It is the result of how privacy policies, infrastructure choices, and legal considerations work together in practice. Many VPNs advertise security, but true protection depends on how these elements are implemented behind the scenes.
To evaluate whether a VPN is genuinely secure, it helps to look at three areas that directly impact user privacy and data protection.
Provider-Level Security Practices
No Logs as a Security Foundation
A secure VPN provider limits data collection at the source. A strict no logs policy means the VPN does not record browsing activity, IP addresses, DNS requests, or connection timestamps. When this information is never collected, it cannot be exposed through breaches, internal misuse, or external requests.
For users, this is one of the strongest indicators that a VPN is built around privacy rather than data monetization.
Independent Audits and Verifiable Claims
Security claims are only meaningful when they can be verified. Independent audits examine whether a VPN’s infrastructure, logging practices, and internal controls align with what the provider publicly states.
Audits add accountability. They provide third party confirmation that privacy policies are enforced in practice, not just written for marketing purposes.
Encryption and Protocol Standards
Encryption and protocol support form the technical backbone of a secure VPN. Providers that prioritize security use modern encryption standards and support protocols that are actively maintained and reviewed by the security community.
This ensures that VPN protection remains effective as threats evolve, rather than relying on outdated or unsupported technologies.
Server and Infrastructure Security
RAM-Only Server Architecture
Infrastructure design plays a major role in VPN security. RAM-only servers operate without persistent storage, meaning data exists only in memory and is erased automatically when a server restarts.
This approach significantly reduces the risk of long-term data retention and limits exposure in the event of physical access or server seizure.
Controlled Access and Ongoing Audits
Strict access controls and routine server audits support secure VPN infrastructure. These practices ensure that only authorized personnel can manage servers and that configurations remain consistent and secure over time.
Regular audits also help identify potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Built-In Leak Protection
Even strong encryption can be undermined by leaks. Secure VPNs implement protections that prevent IP, DNS, and WebRTC leaks, ensuring traffic remains within the encrypted tunnel at all times.
This is particularly important during network changes, such as switching from WiFi to mobile data.
Privacy, Jurisdiction, and Legal Environment
Why VPN Jurisdiction Matters
A VPN provider’s legal location determines which laws govern data handling and user privacy. Some jurisdictions impose mandatory data retention requirements or allow broad government access to user information. Others place stricter limits on surveillance and prioritize individual privacy rights.
Jurisdiction directly affects how easily user data can be requested, compelled, or shared. Even strong technical security can be weakened if local laws require logging or disclosure.
Aligning Legal Structure With Privacy Goals
A secure VPN provider aligns its legal framework with its privacy commitments. This means selecting a jurisdiction that does not require user activity logging and that upholds data protection principles.
AstrillVPN, for example, is based in Liechtenstein, a country known for strong privacy protections and the absence of mandatory data retention laws for VPN services. Operating under such a legal framework supports AstrillVPN’s no logs approach and reduces external pressure to collect or store user data.
While jurisdiction alone does not guarantee security, it plays an important role when combined with transparent policies, strong encryption, and secure infrastructure. Together, these factors reinforce a VPN’s ability to protect user privacy in practice, not just in theory.
VPN Security and Online Threat Protection
VPN security plays an important role in reducing exposure to common online threats, but it is equally important to understand what a VPN can protect against and where its limits lie. A secure VPN strengthens your network layer security by encrypting traffic and masking your IP address, which helps neutralize several everyday risks.
Protection Against Public WiFi Attacks
Public WiFi networks are one of the most common sources of data interception. These networks are often unsecured or poorly configured, making it easier for attackers to monitor traffic or manipulate connections.
A secure VPN encrypts all data before it travels across the network. This prevents attackers on the same WiFi network from reading your traffic, capturing login credentials, or injecting malicious content into your connection.
Reducing ISP and Network-Level Tracking
Without a VPN, internet service providers can see which websites you visit, how long you stay connected, and how much data you use. This information can be logged, analyzed, or shared depending on local regulations.
VPN security limits this visibility by encrypting traffic before it reaches the ISP. While the ISP can see that a VPN connection exists, it cannot see the contents of your online activity, helping reduce passive tracking and profiling.
Defense Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Man-in-the-middle attacks occur when an attacker secretly intercepts communication between a user and a website. These attacks are widespread on public or compromised networks.
By encrypting traffic and verifying server authenticity, a secure VPN makes it significantly more difficult for attackers to intercept or alter data in transit. This added layer of protection helps preserve the integrity of online communication.
What VPN Security Does Not Protect You From?
It is essential to be realistic about VPN capabilities. A VPN does not replace antivirus software or safe browsing habits. It does not prevent phishing attacks, block malicious downloads by default, or protect against compromised websites you willingly interact with.
VPN security strengthens your network connection, but full online protection requires a combination of secure tools and informed user behavior.
VPN Security Best Practices
Even the most secure VPN performs best when it is used correctly. Following best practices helps ensure that VPN security features work as intended and provide consistent protection across different networks and devices.
Choose the Right VPN Protocol for Your Environment
Different protocols are designed for different situations. Some prioritize speed, others focus on stability or censorship resistance.
AstrillVPN, for example, allows users to choose from multiple protocols depending on their environment. Standard protocols such as OpenVPN and WireGuard are well suited for everyday use, while StealthVPN is designed for restrictive networks where VPN traffic may be blocked or inspected.
Selecting the appropriate protocol improves both security and reliability.
Keep the VPN Enabled on Untrusted Networks
A VPN is most effective when it is active before connecting to unsecured or unfamiliar networks. Enabling the VPN on public WiFi, hotel networks, or shared connections helps ensure traffic is encrypted from the moment you connect.
Many secure VPN apps support automatic connection rules that activate protection when an untrusted network is detected.
Use Kill Switch and Leak Protection Features
Kill switch and leak protection features are designed to prevent accidental exposure if a VPN connection drops.
When enabled, these features ensure that:
- Internet traffic is blocked if the VPN disconnects unexpectedly
- DNS requests remain inside the encrypted tunnel
- Your real IP address is not exposed during network changes
Keep VPN Apps and Devices Updated
Security improvements and vulnerability patches are delivered through software updates. Keeping your VPN app, operating system, and devices up to date ensures you benefit from the latest security enhancements.
Outdated software can introduce weaknesses that undermine even strong VPN protection.
Avoid Free VPN Services for Sensitive Activity
Free VPNs often come with limitations that affect security and privacy. Some rely on weaker encryption, limited server infrastructure, or data collection practices that conflict with user privacy.
For sensitive browsing, remote work, or personal communication, a paid secure VPN with transparent policies and modern security practices offers a much higher level of protection.
VPN Security for Different Users and Scenarios
VPN security needs vary depending on how and where the internet is used. A secure VPN should be flexible enough to adapt to different environments, devices, and threat levels without compromising protection. Understanding these scenarios helps users apply VPN security more effectively rather than relying on a one size fits all approach.
VPN Security for Everyday Browsing
For most users, VPN security is about protecting routine online activity. Browsing websites, accessing accounts, and using public networks all expose personal data to tracking and interception.
A secure VPN encrypts traffic, masks the real IP address, and limits visibility from internet service providers and network operators. This reduces passive tracking and helps keep browsing activity private, especially when using shared or unsecured networks.
VPN Security for Public WiFi and Travel
Travelers frequently rely on hotel, airport, and café WiFi networks. These networks are often unencrypted or shared among many users, increasing the risk of interception.
VPN security is especially important in these situations. Encrypting traffic before it leaves the device prevents attackers on the same network from monitoring activity or capturing sensitive information. Automatic connection rules and reliable kill switch features help maintain protection even when networks change.
VPN Security for Remote Work and Professionals
Remote work introduces new security challenges, particularly when accessing company resources outside a controlled office environment.
A secure VPN protects work related data by encrypting connections and preventing exposure on home or public networks. For professionals handling sensitive information, consistent VPN usage helps reduce the risk of data leaks and unauthorized access.
VPN Security for Restrictive or Filtered Networks
In some regions or networks, VPN traffic may be blocked or actively inspected. Standard VPN protocols can struggle in these environments.
AstrillVPN addresses this scenario with proprietary protocols such as StealthVPN, which is designed to disguise VPN traffic as regular internet traffic. This allows users to maintain secure connections even on networks that attempt to restrict VPN usage.
VPN Security on Mobile Devices
Mobile devices frequently switch between WiFi and cellular networks, which can introduce connection instability.
A secure VPN must handle these transitions smoothly while maintaining encryption. Protocols like WireGuard and IKEv2 are well suited for mobile use due to their ability to reconnect quickly without exposing data during network changes.
VPN Security for Streaming and General Use
While streaming is often associated with access rather than security, VPN protection still plays a role. Encrypting traffic helps prevent bandwidth throttling by network providers and protects viewing habits from being logged or profiled.
Secure VPN vs Proxy vs Tor: Security Comparison
Tools like VPNs, proxies, and Tor are often grouped together, but they serve very different security and privacy purposes. Understanding how each works helps clarify which option offers the right level of protection for everyday use.
How a Secure VPN Compares to a Proxy
A proxy acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. It forwards requests and replaces your IP address, but it does not encrypt traffic by default.
A secure VPN, on the other hand, encrypts all data before it leaves your device and routes it through a protected tunnel. This prevents network level interception and hides activity from ISPs and WiFi operators.
From a security standpoint, the difference is significant. Proxies may help with basic IP masking, but they do not protect data from eavesdropping. A secure VPN is designed to protect both identity and data in transit.
Secure VPN vs Tor Network
Tor focuses on anonymity rather than everyday security. It routes traffic through multiple volunteer operated nodes, encrypting it at each step to obscure the origin of the connection.
While Tor offers strong anonymity, it comes with tradeoffs. Connections are significantly slower, some websites block Tor traffic, and exit nodes can still see unencrypted traffic. Tor is best suited for high anonymity scenarios rather than regular browsing or work related use.
A secure VPN provides a more balanced approach. It encrypts traffic, protects against network level threats, and maintains usability for daily activities such as browsing, streaming, and remote work.
Which Option Is More Secure for Everyday Use
For most users, a secure VPN offers the best balance of protection, performance, and usability.
- VPNs encrypt traffic and protect against interception
- Proxies offer limited privacy without encryption
- Tor prioritizes anonymity but sacrifices speed and convenience
Is Using a VPN Legal and Secure?
VPN legality and security are common concerns, especially as privacy awareness grows. In most cases, using a VPN is both legal and secure when used responsibly.
Is Using a VPN Legal?
In most countries, using a VPN is completely legal. VPNs are widely used by individuals, businesses, and organizations to protect data, secure remote access, and enhance privacy.
Some countries restrict or regulate VPN usage, often requiring providers to operate under specific guidelines or limiting how VPNs can be used. In these regions, legality may depend on how the VPN is used rather than the VPN itself.
It is always important to understand local regulations, especially when traveling or working across borders.
Is Using a VPN Secure?
When properly implemented, a VPN is a secure way to protect internet traffic. Security depends on the provider’s encryption standards, infrastructure design, and privacy policies.
A secure VPN encrypts data, verifies server authenticity, and prevents traffic leaks. Providers that invest in modern protocols, strong encryption, and transparent practices offer meaningful protection against common online threats.
AstrillVPN, for example, focuses on strong encryption, multiple protocol options, and infrastructure designed to support privacy. These elements help ensure that VPN security holds up in real world usage.
Legal Use vs Responsible Use
While VPNs enhance privacy and security, they do not make illegal activity legal. Using a VPN responsibly means complying with local laws and service terms while protecting personal data and online communication.
Drawbacks of Using VPNs for Access Control
Using VPNs for access control can be effective, but they are not without limitations. From a security and operational standpoint, there are several drawbacks worth understanding, especially for organizations and teams that rely on VPNs to manage user access.
Limited Granular Access Control
Traditional VPNs typically grant broad network access once a user is authenticated. After connecting, users often gain visibility into large portions of the internal network, even if they only need access to a single application or service. This lack of fine grained control increases the risk of lateral movement if an account is compromised.
Overreliance on Network-Level Security
VPNs focus on securing the network connection rather than individual applications or user contexts. Once inside the network perimeter, access decisions are often less strict. This perimeter-based model can be problematic in modern environments where users, devices, and locations constantly change.
Performance and Latency Issues
Routing traffic through a VPN can introduce latency, especially if servers are geographically distant or overloaded. For access control use cases, this can affect productivity, slow down internal applications, and degrade user experience, particularly for cloud based services.
Scalability Challenges
As organizations grow, managing VPN access becomes more complex. Provisioning users, rotating credentials, and maintaining access rules can be difficult at scale. VPNs were not originally designed for large, distributed workforces with dynamic access needs.
Single Point of Failure Risk
A VPN gateway can become a critical dependency. If it goes offline due to misconfiguration, attack, or infrastructure issues, users may lose access to essential systems. This makes VPN availability and redundancy a key concern in access control scenarios.
Device Trust Assumptions
VPNs often assume that a device is trustworthy once authenticated. They do not inherently verify device posture, security health, or compliance status. If a compromised or unmanaged device connects successfully, it may gain access to sensitive resources.
Increasing Shift Toward Zero Trust Models
Due to these limitations, many organizations are transitioning to zero-trust access models. These approaches focus on continuous verification, identity-based access, and application-level controls rather than broad network access through a VPN.
Conclusion
VPN security plays a crucial role in protecting online activity by encrypting data, concealing IP addresses, and minimizing exposure to tracking and interception. When built on strong encryption, modern protocols, and transparent privacy practices, a secure VPN provides reliable protection across everyday browsing, public WiFi, and remote work scenarios.
At the same time, VPNs are not a complete security solution on their own. They work best when combined with responsible usage and other security tools. Choosing the right VPN means looking beyond marketing claims and focusing on how security is implemented in practice.
With the right approach, VPN security remains one of the most effective ways to maintain privacy and control over your internet connection.
FAQs
To make sure your VPN is secure, start by choosing a provider that uses strong encryption, supports modern protocols, and follows a strict no-logs policy. Verify that the provider has transparent privacy practices and, ideally, independent security audits.
On the user side, keep the VPN app updated, enable features like kill switch and leak protection, and always use the VPN on untrusted networks such as public WiFi. Security depends both on how the VPN is built and how it is used.
No VPN is completely secure in every situation. A VPN significantly improves privacy and protects data in transit, but it does not eliminate all risks.
VPNs secure your network connection, not your behavior or the websites you interact with. Phishing, malware, and compromised services can still pose threats even when a VPN is active. VPN security should be viewed as a strong layer of protection, not a guarantee of total safety.
Organizations can strengthen VPN security by tightening access controls, enforcing strong authentication, and limiting network exposure.
Best practices include using multi-factor authentication, restricting access based on roles, regularly auditing VPN configurations, and keeping VPN software and servers fully updated. Segmenting networks and monitoring access activity also helps reduce the impact of compromised accounts.
VPNs are most effective in organizational settings when combined with broader security policies rather than used as standalone defenses.
Access control determines who can connect to a VPN and what resources they can reach once connected. Strong access control reduces the risk of unauthorized access and limits damage if credentials are compromised.
Effective VPN security relies on verifying user identity, enforcing least privilege access, and regularly reviewing permissions. Without proper access control, a VPN can unintentionally provide broad network access to users who do not need it.
No. A VPN does not protect against all internet threats.
A VPN encrypts traffic and protects against network-level risks such as eavesdropping and interception. It does not block phishing attacks, prevent malware infections, or secure vulnerable websites on its own.
VPNs are best used as part of a broader security approach that includes safe browsing habits, endpoint protection, and regular software updates.


No comments were posted yet