Common VPN Error Codes and How to Fix Them

Arsalan Rathore

Even the most reliable VPN users occasionally encounter connection problems that display confusing error codes. These codes are not random; they indicate specific issues arising from server configuration, network instability, or local software conflicts. Understanding what these error codes mean and how to fix them can save you time, frustration, and unnecessary troubleshooting.
VPN error codes are the system’s way of communicating what went wrong during the connection process. For instance, some errors signal authentication issues, while others may point to server downtime or firewall interference. Each one tells a different story about what’s happening behind the scenes. The good news is that most of these errors are easy to fix once you know their causes and solutions.
This guide’ll explain the most common VPN error codes, how to fix them, and what they mean.
Table of Contents
12 Common VPN Error Codes and their Fixes
VPN error codes can appear intimidating, especially when your connection suddenly drops or refuses to establish. These codes, however, are simply the system’s way of telling you what went wrong. Each corresponds to a specific issue that can usually be fixed with a few adjustments. To help you understand them better, here’s a breakdown of the twelve most common VPN error codes, what causes them, and how you can fix them effectively.
1. Error 619 – Connection to the VPN failed
This error usually occurs when your VPN client tries to establish a connection but fails to reach the VPN server. It often appears after the login process begins, before the secure tunnel is created. Network instability, firewall interference, or incorrect port configurations are usually behind this error.
Fixing Error 619
This error typically indicates interference from firewalls, antivirus tools, or unstable internet connections. Begin by restarting your modem or router and ensuring your internet is active. Temporarily disable any third-party firewall and try reconnecting. If you are using AstrillVPN, switching to another protocol like OpenWeb or StealthVPN can often bypass restrictions that cause Error 619.
2. Error 720 – No PPP control protocols configured
Error 720 points to an issue with the Point-to-Point Protocol, which is responsible for establishing the VPN link. This happens when the TCP/IP settings are misconfigured or the system’s network protocols are damaged. It’s a common issue on Windows-based VPN connections.
Fixing Error 720
To fix Error 720, reset your TCP/IP stack and reinstall network protocols. This can be done on Windows by opening Command Prompt and typing “netsh int ip reset.” AstrillVPN automatically configures the correct network settings during installation, so reinstalling the app can resolve protocol-related errors.
3. Error 800 – Unable to establish a connection to the VPN server
One of the most frequent VPN errors, Error 800 occurs when your device cannot communicate with the VPN server. This could happen if the server address is incorrect, the internet connection is unstable, or the VPN server is temporarily unavailable.
Fixing Error 800
Error 800 often appears when the VPN server address is incorrect or unreachable. Verify that you entered the correct hostname and that your device is connected to the internet. If the server is under maintenance, switching to a nearby AstrillVPN server usually restores connectivity.
4. Error 806 – The VPN connection was established but the connection failed
This error means your device successfully connected to the VPN server but failed to complete the data tunnel. The most likely causes are blocked GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) traffic or firewalls interfering with VPN ports.
Fixing Error 806
This error means GRE traffic is being blocked. You can enable VPN passthrough on your router or check if your firewall is blocking PPTP or L2TP connections. AstrillVPN’s OpenWeb and StealthVPN protocols do not rely on GRE, so changing protocols can quickly solve this problem.
5. Error 809 – The network connection between your computer and the VPN server could not be established
Error 809 often indicates that a firewall or router is blocking the ports the VPN protocol requires. It can also happen if the server is behind a NAT (Network Address Translation) device that does not support VPN passthrough.
Fixing Error 809
Blocked ports or strict firewalls commonly cause error 809. To fix it, open the required ports or use AstrillVPN’s StealthVPN protocol, which is designed to disguise VPN traffic and pass through restrictive firewalls using standard ports like TCP 443.
6. Error 812 – Authentication policy mismatch
This error occurs when the VPN server’s authentication method does not match what the client is configured to use. It could also happen if the user’s credentials are not authorized for remote access under the server’s policy settings.
Fixing Error 812
This error happens when the authentication method does not match the VPN server’s policy. Ensure your username and password are correct and your account has remote access permission. AstrillVPN users should also confirm that their account subscription is active and that no custom authentication settings are altered in the app.
7. Error 691 – Access denied due to invalid credentials
A very straightforward error, 691 means that the VPN server rejected your login attempt because of an incorrect username or password. Sometimes, it can also occur if the user’s account has been disabled or is restricted by group policy.
Fixing Error 691
Double-check your login credentials. If your AstrillVPN password has been recently updated, ensure it matches all devices. Occasionally, this error can occur if your ISP or workplace uses restrictive networks, so switching to a protocol like StealthVPN can help.
8. Error 734 – PPP link control protocol terminated
Error 734 signals that the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) failed during negotiation. It usually appears when there’s an issue with the authentication protocol, such as CHAP or PAP, or a mismatch between client and server.
Fixing Error 734
To fix this, adjust the authentication protocol settings on your VPN connection. Depending on your configuration, ensure CHAP or PAP is enabled. AstrillVPN manages these settings automatically, so reinstalling or updating the app can eliminate this issue.
9. Error 789 – L2TP connection attempt failed due to security layer error
This Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) error typically occurs when IPsec (which provides encryption for L2TP) fails to initialize. The issue might stem from a missing certificate, a misconfigured pre-shared key, or interference from third-party security software.
Fixing Error 789
This error indicates that IPsec could not initialize correctly. Verify that your system clock is accurate and that the correct pre-shared key or certificate is configured. AstrillVPN simplifies this process with built-in, pre-validated certificates that remove the need for manual setup.
10. Error 868 – The remote connection was not made because the name of the remote access server did not resolve
Error 868 appears when the VPN client cannot translate the server’s hostname into an IP address. In other words, a DNS-related problem prevents your system from finding the VPN server.
Fixing Error 868
Error 868 usually stems from DNS issues. Restart your router or switch to a more reliable DNS resolver. AstrillVPN includes built-in DNS leak protection and private DNS servers, ensuring all queries remain encrypted and properly routed through the VPN.
11. Error 812 – The connection was prevented because of policy configuration
While similar to other authentication errors, this version of Error 812 occurs specifically when the network policy server blocks the connection based on user group or authentication type. It can appear after a network admin changes security settings.
Fixing Error 812 (Policy Configuration Restriction)
If you encounter this version of Error 812, check your network policies or user group permissions. AstrillVPN users rarely face this problem since the app’s built-in authentication system bypasses local policy conflicts. However, ensuring you are not running AstrillVPN under restricted administrative controls is still essential.
12. SSL and Certificate Errors
Beyond numbered error codes, SSL and certificate-related errors are among the most common in modern VPNs that rely on secure tunneling. They occur when a certificate is expired, self-signed, or mismatched with the server domain. Many clients treat such certificates as untrustworthy, causing the connection to fail even though the network is fine.
Fixing SSL and Certificate Errors
The system cannot verify the VPN server’s identity when certificate warnings appear. Avoid connecting to unverified servers and only use official AstrillVPN servers, which use trusted, up-to-date SSL certificates. If you are on a corporate or custom setup, check for expired or mismatched certificates in the VPN configuration.
Advanced VPN Error Troubleshooting
When standard troubleshooting steps do not solve the issue, it’s time to move into advanced VPN diagnostics. These techniques dig deeper into your system’s configuration, network behavior, and encryption layers to identify the cause of persistent connection problems. With AstrillVPN, users have the advantage of a robust set of tools and advanced protocol options that make pinpointing and resolving issues easier and faster.
1. Analyze VPN Logs for Technical Clues
VPN logs record every attempt to connect, authenticate, and establish tunnels. Examining these logs allows you to determine whether the failure happens during authentication, handshake, or data transmission. AstrillVPN provides detailed connection logs that help users and support staff quickly locate where the process breaks down.
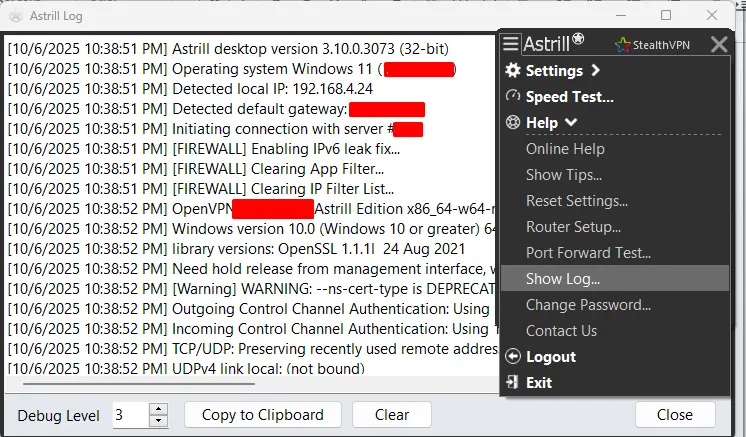
For example, a log entry showing a TLS handshake failure may indicate a certificate or protocol mismatch, while a timeout could suggest blocked ports.
2. Test Different VPN Protocols
Each VPN protocol operates differently. OpenWeb, for example, is lightweight and optimized for speed, while StealthVPN is designed to bypass deep packet inspection and restrictive firewalls. If a connection fails consistently under one protocol, switching to another can reveal whether the issue is related to port blocking, encryption, or ISP interference.
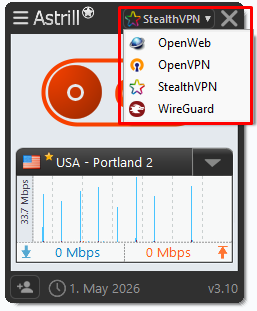
AstrillVPN allows seamless switching between OpenWeb, StealthVPN, WireGuard, and OpenVPN directly from the app interface, helping users instantly adapt to any network environment.
3. Perform Port and Firewall Diagnostics
Advanced users can test whether the necessary ports are open or blocked on their network. AstrillVPN relies on specific ports for its protocols, and if a router or corporate firewall blocks them, connections can fail.
Tools like Telnet, Nmap, or Windows PowerShell can help check port accessibility. If specific ports are restricted, switching to a different protocol, such as StealthVPN, can route traffic through commonly open ports, allowing the VPN to connect even under strict network conditions.
4. Verify Certificate and Encryption Settings
SSL or TLS-based VPNs rely on digital certificates to verify the server’s identity and establish a secure tunnel. The VPN client may refuse to connect if a certificate is expired, mismatched, or self-signed. To prevent such issues, AstrillVPN uses valid, secure certificates for all its servers. Still, users on custom or enterprise setups should ensure their system clocks are accurate and that no local SSL interception software is altering certificates.
5. Inspect DNS and IP Routing Conflicts
In some cases, DNS leaks or routing conflicts can disrupt VPN sessions. A common symptom is that the VPN connects successfully, but users cannot browse or reach certain websites. AstrillVPN includes built-in DNS leak protection and Smart Mode routing, which ensure that DNS requests and IP traffic always follow secure VPN tunnels. Advanced users can also run “tracert” or “ping” commands to identify where packets are being dropped along the route.
6. Use Network Monitoring Tools
Network analyzers like Wireshark can reveal packet behavior during connection attempts. By inspecting whether encrypted packets reach the VPN server, users can identify whether interference occurs at the router, ISP, or endpoint. AstrillVPN’s advanced protocols like StealthVPN and OpenWeb are specifically designed to disguise VPN traffic, ensuring network providers cannot easily detect or throttle it.
7. Reset Network Stack and DNS Cache
Over time, corrupted network configurations can interfere with VPN communication. Flushing the DNS cache, resetting the TCP/IP stack, or renewing the IP address can often eliminate deep-seated conflicts. AstrillVPN works best on clean, properly configured network stacks with no conflicting proxy or security software.
8. Check for Device-Specific or OS-Level Restrictions
Some operating systems and devices have built-in network filters or policies that affect VPN performance. For instance, Windows group policies or macOS firewall rules can limit VPN access. AstrillVPN’s multi-platform support ensures compatibility across Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. Still, users should verify that their operating system is fully updated and that VPN processes are not blocked in the background.
9. Review Router and Modem Settings
Routers with outdated firmware, double NAT configurations, or disabled VPN passthrough can cause recurring connection failures. Access your router settings and ensure VPN passthrough is enabled for IPsec, L2TP, or PPTP if applicable. AstrillVPN also allows users to configure VPN connections directly on supported routers, ensuring that all connected devices are protected at the network level.
10. Contact AstrillVPN’s Expert Support Team
Even the most advanced users sometimes encounter complex networking problems that require deeper analysis.
AstrillVPN’s technical support team is available around the clock to assist with detailed diagnostics, configuration verification, and advanced log interpretation. Their expertise ensures that even the most persistent or environment-specific issues are resolved efficiently.
VPN Error Codes on Mobile Devices
Mobile devices often handle VPN connections differently from desktop systems. Their smaller operating systems, mobile networks, and power management settings can create unique challenges that trigger VPN errors. Whether you are using Android or iOS, understanding how these errors appear and what causes them helps ensure a smoother mobile VPN experience.
AstrillVPN’s mobile apps are designed to minimize these issues, but here are the most common mobile-specific VPN errors and what they mean.
1. “VPN Connection Failed” or “Cannot Connect to Server” (iOS and Android)
This is the most common mobile VPN error. It usually occurs when the device cannot reach the VPN server because of poor mobile data connectivity, an unstable Wi-Fi network, or incorrect VPN configuration. AstrillVPN’s mobile app automatically retries the connection and can switch between servers to find the most stable route, reducing the likelihood of this issue.
2. “Authentication Failed” or “Login Error”
If you see this message on your phone, your credentials may not have synced correctly, or your VPN profile may have been corrupted during setup. Log out of the app, re-enter your AstrillVPN username and password, and try connecting again. Ensure that your subscription is active and your phone’s date and time are correct, as time mismatches can affect authentication.
3. “The VPN Configuration Could Not Be Installed” (iOS)
This error often appears when installing or reconfiguring a VPN profile. It can happen if you declined the app’s permission to add VPN configurations or if iOS security settings blocked it. Go to your phone’s Settings, open VPN & Device Management, and allow AstrillVPN to manage VPN profiles. Then, reinstall the app to ensure all configurations are correctly applied.
4. “Connection Timed Out” (Android)
Android devices may display this error when the VPN tunnel fails to initialize within a specific time limit. It usually occurs on weaker mobile networks or when background battery optimization restricts the VPN app’s activity. Disable battery optimization for AstrillVPN, ensure the app runs in the background, and try switching to another protocol, such as OpenWeb or WireGuard for faster connection establishment.
5. “Server Unreachable” or “Server Not Responding”
IP addresses and routes are reassigned automatically when mobile networks change between Wi-Fi and cellular data. If the VPN tunnel cannot adjust quickly, the connection drops, and this error appears. AstrillVPN’s intelligent reconnect feature detects network changes in real time and automatically re-establishes a secure connection without requiring manual intervention.
6. “Connection Reset by Peer”
This error means the VPN server terminated the session unexpectedly. It might happen due to temporary server congestion, protocol conflicts, or unstable data links. In such cases, changing to a different AstrillVPN server or using StealthVPN, which adapts well to mobile environments, often restores stability.
7. “VPN Keeps Disconnecting” or “Drops Frequently”
Mobile devices are prone to intermittent connections because of power-saving features and fluctuating signals. To minimize disconnections, ensure AstrillVPN’s “Always On” or “Auto Connect” feature is enabled. This keeps the VPN active even when switching networks or when the device goes into sleep mode.
8. “Network Blocked” or “VPN Restricted” (on public Wi-Fi or mobile carriers)
Some public Wi-Fi networks or mobile carriers block VPN traffic altogether. The device shows a general connection error without a specific code when this happens. AstrillVPN’s StealthVPN protocol is designed to bypass these restrictions by disguising VPN traffic as normal HTTPS data, allowing uninterrupted access even on restricted networks.
Why AstrillVPN Minimizes VPN Errors
AstrillVPN is designed to deliver a stable, seamless, and secure connection experience by minimizing the chances of VPN errors before they even occur. Unlike many VPN providers relying on shared third-party infrastructure, AstrillVPN operates its dedicated server network with optimized configurations. This ensures fewer connection drops, certificate mismatches, or protocol failures that users commonly face with other VPNs.
Here’s how AstrillVPN reduces VPN errors effectively:
- AstrillVPN runs its own servers instead of relying on external providers, ensuring consistent performance and stability.
- Each server is continuously monitored, and users are connected to the least congested server automatically.
- The app switches between OpenWeb, StealthVPN, WireGuard, and OpenVPN based on network conditions to prevent blocks or instability.
- AstrillVPN uses trusted digital certificates and strong encryption to eliminate SSL and certificate-related errors.
- Users can quickly identify and troubleshoot issues within the app without needing advanced technical knowledge.
- A dedicated support team is always available to resolve complex cases in real time.
Conclusion
VPN errors can be frustrating, especially when you rely on your connection for privacy, work, or streaming. However, most errors are not as complex as they appear once you understand what causes them. From authentication issues and certificate mismatches to DNS problems and connection timeouts, each error has a specific trigger and a clear path to resolution.
By following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide, you can resolve most connection errors and keep your VPN running smoothly. Yet, prevention is always better than constant fixing, and that is where AstrillVPN truly stands out.
FAQs
VPN error codes indicate specific issues preventing a secure connection between your device and the VPN server. Each code represents a unique problem, such as authentication failure, server timeout, or network configuration error.
Frequent VPN errors usually occur due to poor network connectivity, outdated VPN software, incorrect login details, or server overload. Switching to a different server or protocol often resolves the issue.
One of the most common VPN error codes is Error 619, which means the connection to the remote computer could not be established. This typically happens when a firewall or antivirus blocks the VPN connection.
Certificate or SSL errors usually occur when the VPN server’s certificate is invalid or expired. You can fix this by updating the VPN client, verifying system time settings, or reinstalling the certificate from a trusted source.
Different devices may have varying network configurations, cached DNS records, or protocol compatibility issues. Resetting the VPN app or clearing the network cache can often fix the issue.


No comments were posted yet