What is a VPN Client? It’s Types and All You Need to Know About It
Want to know what is a VPN client and what does it do? In today’s digital world, online security matters more than ever. This guide covers all the important aspects of a VPN client, VPN types, and how it works. Make sure you go through the guide thoroughly to understand the importance of
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is a VPN Client?
A VPN client is a software application that enables users to connect to a VPN for secure and private internet browsing. It serves as the user interface through which individuals access the VPN network, allowing them to establish a secure connection to a remote server.
The primary function of a VPN client is to encrypt the user’s internet traffic, ensuring that data transmitted between the user’s device and the VPN server remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access or surveillance.
How Does a VPN Client Work?
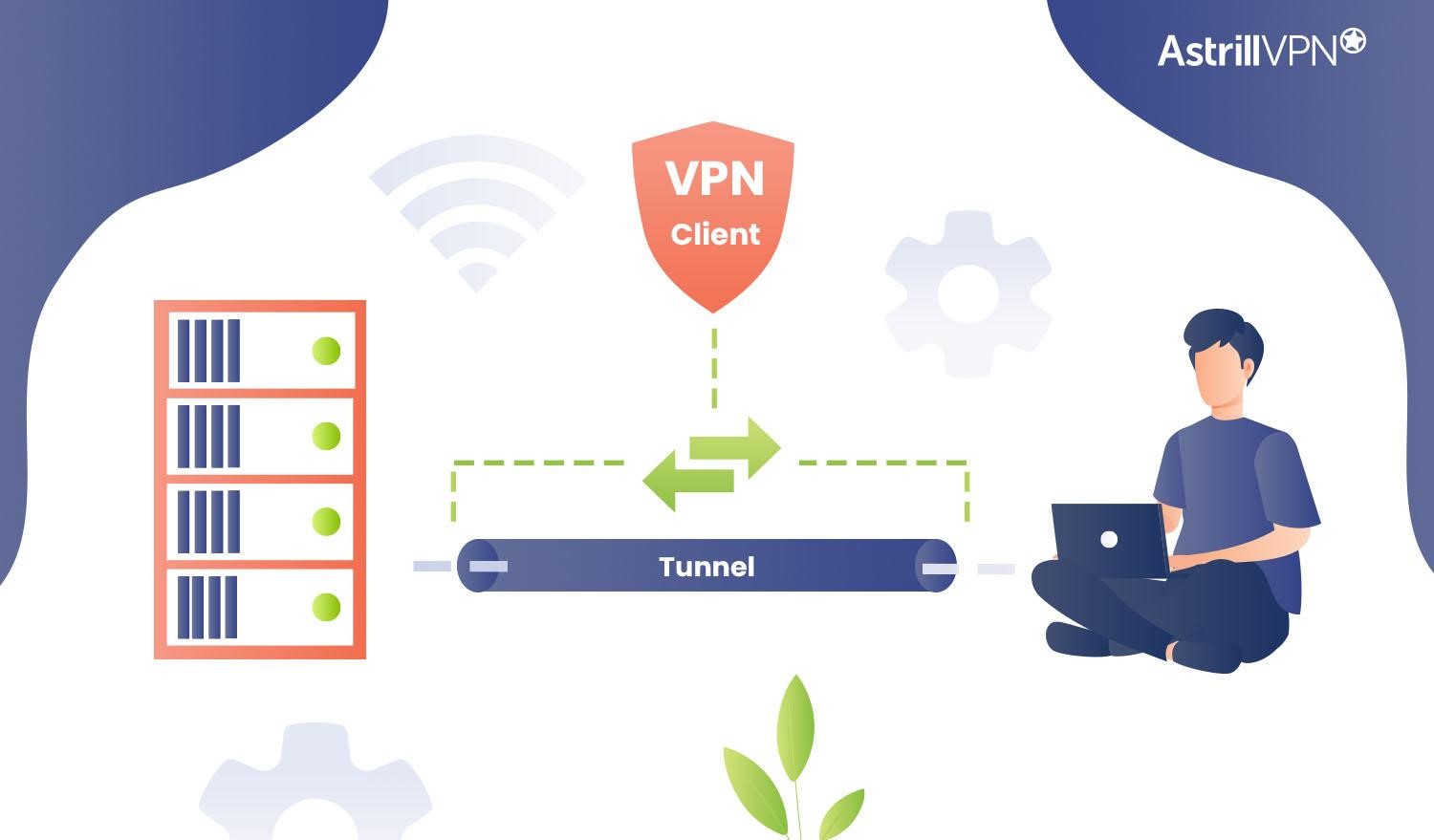
A VPN client operates by establishing a secure tunnel between the user’s device and the VPN server. When a user activates the VPN client, the software encrypts all outgoing internet traffic from the device before it reaches the internet service provider (ISP).
This encrypted data is then transmitted through the VPN tunnel to the VPN server, decrypted, and sent to the intended destination on the internet. Importantly, this encryption process shields users’ online activities from potential eavesdropping, hacking attempts, or third-party monitoring.
Moreover, VPN clients utilize different encryption protocols (such as OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, or IKEv2/IPsec) to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over the VPN connection. Additionally, by masking the user’s IP address with that of the VPN server, VPN clients provide anonymity and enable bypassing geo-restrictions, allowing users to access content and services that might otherwise be inaccessible in their geographical location.
Overall, a VPN client is the intermediary tool that facilitates a secure and private connection to a VPN server, offering users enhanced online security and the freedom to browse the internet with increased anonymity and privacy.
Why Use a VPN Client?
A VPN client offers many benefits, making it a crucial tool for individuals and organizations seeking enhanced online privacy, security, and accessibility. Here are some key reasons why utilizing a VPN client is advantageous:
● Features
VPN clients often come equipped with various features tailored to meet user needs. These may include robust encryption protocols, multiple server locations worldwide, kill switch functionality, and ad-blocking capabilities.
The versatility of features enables users to customize their VPN experience based on specific requirements, whether for securing sensitive data, accessing geo-blocked content, or ensuring anonymity while browsing.
● Customization
One significant advantage of VPN clients is their flexibility and customization options. Users can typically configure settings within the VPN client, such as choosing preferred encryption protocols, selecting specific servers or regions, and adjusting security settings to align with their privacy preferences.
This customization empowers individuals to tailor their VPN connection to their unique online activities and security concerns.
● Ease-of-use
VPN clients are designed to be user-friendly, providing a straightforward interface allowing easy activation, connection, and disconnection from the VPN network. The simplicity of these applications ensures that even those without technical expertise can navigate and utilize the VPN service effectively.
With intuitive controls and clear instructions, users can establish secure connections with minimal effort. If you look at AstrillVPN’s app interface for any device, you’ll notice that it’s very easy to select a server, protocol and establishing the connection to its server.
● Information
VPN clients offer a layer of security by encrypting data transmitted over the internet. This encryption safeguards sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal details, financial transactions, and browsing history, from potential interception by cybercriminals, ISPs, or other entities seeking to monitor or exploit online activities.
● Authentication
VPN clients integrate robust authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) or secure login protocols, to further fortify user access.
These authentication layers bolster the overall security of the VPN connection, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the VPN network and its resources.
● Split tunneling
AstrillVPN clients feature split tunneling features in the form of a Web filter and an App filter. This functionality allows users to direct part of their internet traffic through the encrypted VPN tunnel while accessing the internet without the VPN for specific applications or websites.
This feature offers greater flexibility, enabling users to maintain secure connections for sensitive activities while accessing local services or devices outside the VPN.
Types of VPN clients
Various types of VPN clients are available, each catering to specific devices, operating systems, or user preferences. Below are the common types of VPN clients:
1. Desktop VPN Clients
Desktop VPN clients are software applications for computers and laptops running Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems. These clients offer a user-friendly interface, allowing users to easily connect VPN client and server, choose server locations, configure settings, and manage their VPN connections. They often provide comprehensive features and encryption protocols for secure browsing.
The best example is AstrillVPN’s user-friendly VPN app for Windows, which has all the options like servers and protocols upfront and allows users to connect to a VPN server without any hassle.
2. Mobile VPN Clients
Mobile VPN clients are applications developed for smartphones and tablets, supporting operating systems such as iOS and Android. These apps offer similar functionalities to desktop clients, enabling users to establish secure connections while on the go. Mobile VPN clients are essential for safeguarding sensitive data when using public Wi-Fi networks and ensuring privacy on mobile devices.
3. Browser-Based VPN Extensions
Browser-based VPN extensions are lightweight add-ons that integrate directly into web browsers like Google Chrome, Firefox, or Safari. These extensions offer a quick and convenient way to enable VPN functionality within the browser, allowing users to encrypt their browser traffic and access geo-blocked content without needing a separate application.
4. Router-Level VPN Clients
Some advanced routers come equipped with VPN client capabilities. Users can configure their routers to connect to a VPN server, thereby extending the VPN protection to all devices connected to the network. This setup is beneficial for securing smart home devices, gaming consoles, or IoT devices that do not have native VPN support.
5. Command-Line Interface (CLI) VPN Clients
CLI VPN clients are text-based interfaces that allow users to interact with the VPN software using commands typed into a terminal or command prompt. These clients are often preferred by advanced users or system administrators who require specific configurations or scripting capabilities for automation purposes.
6. Corporate or Enterprise VPN Clients
Large organizations often use specialized VPN clients tailored to their security and management needs. These clients offer features like centralized control, policy enforcement, and integration with corporate authentication systems. They ensure secure remote access for employees while maintaining compliance with company policies and security standards.
VPN server vs VPN client
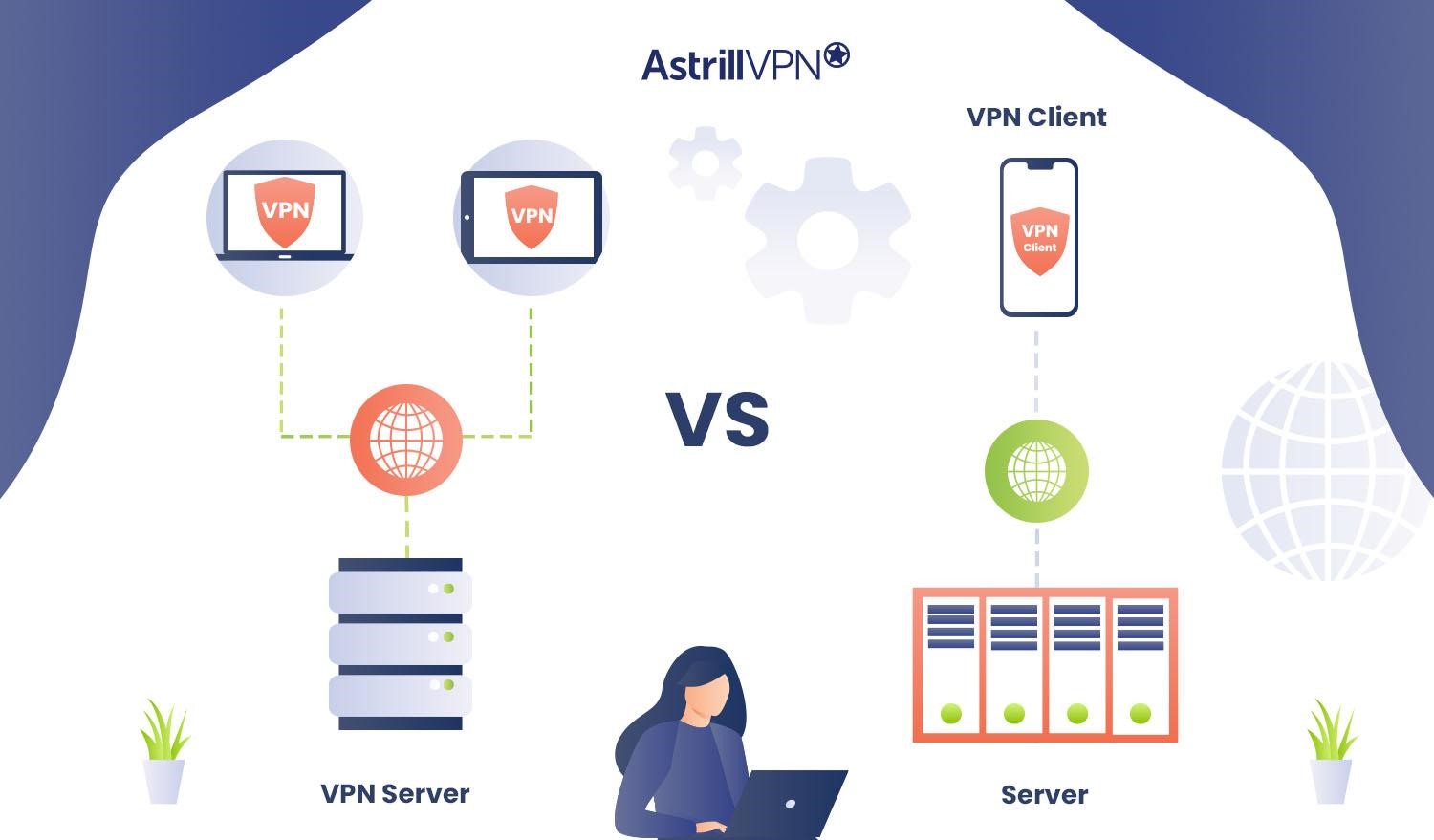
A VPN server is a remote gateway that manages and facilitates incoming VPN connections. It operates within a VPN service provider’s infrastructure or an organization’s network. This server is responsible for receiving encrypted data from VPN clients, decrypting it, and routing it to the internet. Similarly, it receives incoming data from the internet, encrypts it, and securely transmits it back to connected VPN clients.
VPN servers are strategically located in various global regions, allowing users to connect to different server locations for accessing region-specific content or optimizing connection speeds. Furthermore, VPN servers ensure security by encrypting and decrypting data traffic, providing users anonymity and privacy protection.
On the other hand, a VPN client is software installed on a user’s device, such as a computer, smartphone, or tablet. Its primary function is to initiate a secure connection to a VPN server, establishing a protected tunnel through which internet traffic is transmitted.
When activated, the VPN client encrypts all outgoing data from the device before sending it to the VPN server. Upon receiving data from the server, the client decrypts it, allowing the user to access the information. VPN clients are essential in securing online activities by encrypting data, ensuring privacy, and anonymizing the user’s IP address.
They enable users to connect to VPN servers, providing a secure pathway for internet traffic and ensuring a safer online browsing experience.
Technical specifications for VPN clients
Here are the technical specifications and requirements for VPN clients across different operating systems:
Requirements for the Windows VPN client
- Operating System: Compatible with various versions of Windows (e.g., Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10)
- Protocols Support: Should ideally support multiple protocols such as OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, IKEv2/IPsec, and PPTP for compatibility and flexibility.
- Encryption Strength: Should offer robust encryption methods such as AES 256-bit encryption for secure data transmission.
- User Interface: User-friendly interface for easy configuration and management of VPN connections.
- Kill Switch: Capability to include a kill switch feature for automatic disconnection if the VPN connection drops, preventing data leakage.
- Split Tunneling (Optional): Some users require this feature for routing specific traffic through the VPN while allowing other traffic directly through the ISP.
Requirements for the macOS VPN client
- Operating System: Compatible with macOS versions like Catalina, Big Sur, and subsequent releases.
- Protocol Support: Similar to Windows, supporting OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPsec, L2TP/IPsec, and other secure protocols for connectivity.
- Strong Encryption: Similar robust encryption standards like AES 256-bit encryption to ensure data security.
- Seamless Integration: Integration with the macOS environment, offering an intuitive interface and ease of use for Mac users.
- DNS Leak Protection: Should protect against DNS leaks to ensure complete privacy.
- Customization Options: Ability to configure settings and preferences as per user requirements.
Requirements for Linux VPN client
- Diverse Distribution Support: Compatible across various Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Fedora, and Debian.
- Open Source Availability: Often preferred to have open-source clients for transparency and community support.
- Protocol Compatibility: Support for OpenVPN, PPTP, and other protocols commonly used within the Linux environment.
- Command-Line Interface (Optional): Advanced users may prefer command-line interface capabilities for manual configurations.
- Security Updates: Regular updates and patches to ensure security and compatibility with newer Linux kernel versions.
Requirements for iOS VPN client
- Operating System: Compatibility with iOS devices (iPhone, iPad) running the latest iOS versions.
- Protocol Support: Native support for IKEv2/IPsec and L2TP/IPsec for easy configuration on iOS devices.
- Integrated Settings: Smooth integration with the iOS settings menu for straightforward setup and management.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive interface suitable for mobile devices ensures easy use and quick connectivity.
- App Store Availability: Available through the Apple App Store for easy installation and updates.
Requirements for Android VPN client
- Operating System: Compatibility with Android devices running various versions (Android 8, 9, 10, etc.).
- Protocol Support: Native support for IKEv2/IPsec and L2TP/IPsec, similar to iOS, for easy configuration.
- Interface Adaptability: Adaptive interface design for different Android smartphone and tablet screen sizes and resolutions.
- Battery Efficiency: Optimized to consume minimal battery while maintaining a stable VPN connection.
- Google Play Availability: Easily accessible and downloadable through the Google Play Store for updates and installations.
Free vs. paid VPN client
When considering free versus paid VPN clients, several crucial factors differentiate the two options:
Free VPN Clients
- Limited Features and Functionality: Free VPN services usually have restricted features, limited server choices, and capped data usage. The range of available servers and locations might be significantly fewer than paid versions.
- Privacy Concerns and Data Logging: Many free VPNs fund their services by logging user data and selling it to advertisers or third parties. This practice compromises user privacy and contradicts the purpose of using a VPN for anonymity and security.
- Security Risks and Weak Encryption: Free VPNs might lack robust encryption protocols, leaving users vulnerable to cyber threats. They could also lack essential security features such as kill switches or DNS leak protection, increasing the risk of data exposure.
- Performance and Speed Issues: Due to many users sharing limited resources, free VPNs often suffer from slower speeds and frequent connectivity issues, impacting user experience, especially during peak hours.
- Advertisement and Revenue Model: Free VPNs commonly rely on advertising or upselling premium versions, bombarding users with ads, or restricting access to certain features to encourage upgrades to their paid plans.
- Potential Legality and Trust Issues: Some free VPNs might engage in shady practices, like routing user traffic through botnets or engaging in illegal activities, raising concerns about their credibility and legality.
Paid VPN Clients
- Enhanced Features and Comprehensive Services: Paid VPNs offer a wide array of features, such as unlimited bandwidth, faster speeds, a larger server network, and additional security measures like split tunneling, dedicated IP addresses, and more.
- Privacy and No-Logs Policy: Reputable paid VPN services adhere to strict no-logs policies, ensuring user data isn’t stored or sold. This commitment to privacy helps maintain anonymity and confidentiality.
- Robust Security Measures: Paid VPNs invest in top-tier security, implementing strong encryption standards, secure protocols, and additional features to prevent IP, DNS leaks, or malware attacks, ensuring a more secure browsing experience.
- Reliable Performance: Due to dedicated resources and fewer users sharing servers, paid VPNs generally offer stable and consistent performance, maintaining optimal speeds and uptime.
- Customer Support and Service Quality: Paid VPN services typically provide dedicated customer support through various channels, including live chat, email, or phone, offering prompt assistance and troubleshooting.
- Transparent and Legitimate Operations: Legitimate paid VPN services operate transparently, providing clear terms of service and maintaining trust by adhering to ethical business practices.
Should you configure your VPN manually?
Configuring a VPN manually involves setting up the VPN connection without relying on the VPN provider’s dedicated client. This method may suit users with specific preferences or advanced technical knowledge. Consider the following:
- Advanced Customization: Manual configuration allows for fine-tuning security settings and choosing preferred protocols or encryption methods, catering to specific security needs.
- Device Compatibility: Some devices or platforms may not have native VPN clients, requiring manual setup for establishing a VPN connection.
- Complexity and Expertise: Manual configuration involves technical steps like entering server details, configuring protocols, and managing settings, which might be challenging for beginners.
- Potential Risks: Incorrect configuration may lead to security vulnerabilities, including IP leaks or misconfigured settings, compromising the effectiveness of the VPN.
Uses of a VPN
The uses of a VPN are extensive and varied, catering to both personal and professional needs like:
Enhanced Online Security and Privacy
VPNs are critical for enhancing online security by encrypting internet traffic and safeguarding sensitive information from potential threats. Utilizing encryption protocols, VPNs ensure that data transmitted between a user’s device and the VPN server remains inaccessible to unauthorized entities, protecting against hackers, cybercriminals, and any form of surveillance.
This encryption shields valuable information, such as financial transactions, personal data, and login credentials, preserving their confidentiality and integrity. Additionally, by masking the user’s IP address and online activities, VPNs offer a layer of anonymity, preventing websites, ISPs, or advertisers from tracking and profiling user behavior for targeted advertising or monitoring.
Accessing Geo-Restricted Content and Bypassing Censorship
One of the prominent utilities of VPNs is their ability to bypass geo-restrictions and access content otherwise limited to specific regions. By changing the user’s virtual location, VPNs allow access to region-locked streaming services, websites, or online platforms like Netflix, Disney Plus, Hulu, etc., enabling users to enjoy a more comprehensive range of content irrespective of their physical location.
Moreover, in regions with strict internet censorship, VPNs facilitate unrestricted access to information, social media, or news websites, offering a means to bypass government-imposed restrictions and ensuring access to an open and free internet.
Secure Remote Access and Business Use
VPNs are crucial in providing secure remote access for employees outside the traditional office environment. They create a secure and encrypted connection between remote devices and a company’s network, ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive corporate data and communications.
Additionally, in business settings, VPNs are integral for establishing secure connections between different office locations, facilitating secure data transfer and communication, and maintaining the integrity of proprietary information.
Protection of Public Wi-Fi Networks
When connected to public Wi-Fi networks prone to security vulnerabilities, VPNs act as a shield by encrypting data traffic. This encryption prevents potential cyber threats, such as eavesdropping or data interception by malicious actors lurking on these open networks.
By encrypting the data transmitted between the user’s device and the VPN server client, VPNs mitigate the risks associated with public Wi-Fi hotspots in cafes, airports, or hotels.
Torrenting and P2P File Sharing
VPNs offer an additional layer of security and anonymity for users engaged in peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing or torrenting. By masking the user’s IP address and encrypting data traffic, VPNs protect against monitoring or throttling of download speeds by ISPs or copyright enforcement agencies, allowing users to engage in these activities with greater privacy and security.
Gaming and Reduced Latency
In the realm of online gaming, VPNs serve multiple purposes. They help mitigate risks associated with Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks by providing protection against such threats during gaming sessions.
Additionally, VPNs enable gamers to access region-locked games or early releases by changing their virtual location to a region where the game is available, enhancing their gaming experience. Furthermore, some gamers leverage VPNs to reduce latency or bypass network restrictions imposed by certain gaming servers or regions.
Price Comparison and Online Shopping
VPNs are instrumental for price-sensitive consumers seeking fair deals and avoiding price discrimination while shopping online. By altering their virtual location, users can access better deals, compare prices across different regions, and avoid being targeted by price discrimination tactics employed by some online retailers based on the user’s geographical location.
Safe and Private Communication
A VPN ensures secure and encrypted communication over various platforms, including messaging apps, emails, or Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services. This encryption shields sensitive conversations and data, maintaining confidentiality and ensuring privacy during online communications.
FAQs
The best example of a VPN client is AstrillVPN’s app for Windows or Android, which users use to establish a secure connection to a VPN server.
A VPN is a network technology that enables secure and encrypted communication over the Internet by creating a private network from a public Internet connection. On the other hand, a VPN client refers to the software application or tool used to connect to a VPN network.
When used correctly, VPNs can significantly enhance online safety and privacy. They encrypt internet traffic, provide a secure tunnel for data transmission, and mask the user’s IP address, enhancing anonymity.
A VPN can be configured either on a router or on individual devices. When set up on a router, all devices connected automatically benefit from the VPN’s encryption and security features.


No comments were posted yet